In this post we will see the step-by-step detail of How to Integrate SAP EWM Warehouse in 7 Easy Steps
Time needed: 30 minutes
How to Integrate SAP EWM Warehouse in 7 Easy Steps
- Step 1 – EWM Warehouse definition and assignment to the Logistics Execution (LE) Warehouse.
In this step we will define EWM warehouses for our car business and assign these to the LE warehouse. We will also acknowledge Use of the advanced functions for our warehouses.
- Step 2 – Assignment of Organizational units to the EWM warehouse
In this step we will configure Supply Chain Unit (SCU) for plants & shipping points and then we will maintain the Supply Chain Hierarchy. We will also configure custodian & party entitled to dispose from both Embedded EWM as well as Decentralized EWM point of view.
- Step 3 – Assignment of EWM stock types & availability group to the S4/EWM Plants and Storage Locations.
In this step we will configure availability groups, their relationship to the stock types/storage types & finally Map Storage Locations from ERP/S4 System to the EWM
- Step 4 – Warehouse-dependent Number Ranges
In this step we will define number ranges for Warehouse Tasks, Waves, Warehouse Orders, Consolidation groups, Physical Inventory Documents & HU Identification etc. We will assign these number ranges to our warehouse.
- Step 5 – LE/ERP-EWM Delivery Document Integration.
In this step we will assign ERP/LE delivery document type & Item type to the EWM warehouse request. Besides this the other supported configuration like number range for LE documents etc. are configured.
- Step 6 – extra step only for Decentralized EWM on S4 HANA
In this step we will configure all the control parameters for decentralized EWM related to version control like, delivery creation in EWM, batch creation in EWM etc.
- Step 7 – Cross Landscape Distribution (XLD) for Decentralized S4 HANA EWM
In this step we will see the synchronization required between S4 & Decentralized EWM.
This post is third in series of “Configure EWM in SAP S4 HANA”.
You may check the below two posts in sequence before proceeding further to this post.
First Post
S4 HANA EWM System Connection: Basic Settings in 3 Easy Steps
Second Post
An Ultimate Guide for Initial S4 Settings to Configure EWM
Below is the anchor post which explains all the steps required to configure Embedded as well as Decentralized EWM in S4 HANA. Configure EWM in SAP S4 HANA
Table of Contents
1. S4 HANA Decentralized or Embedded EWM
By default, please consider that until difference is not specified, the configuration step is same for embedded EMW & Decentralized EWM. The only point to be noted that in case of S4 HANA embedded EWM, all these configuration steps will be executed in the S4 system where all other components like -SD, MM etc. exists while in the case of decentralized EWM on S4 HANA, these steps will be executed in the decentralized EWM instance.
The last two steps in this post are exclusively for decentralized EWM. You can ignore these steps if you are using an embedded EWM.
2. EWM Warehouse definition and assignment to the Logistics Execution (LE) Warehouse
This is the third series in the configuration of EWM in S4 HANA.
You may Please check the previous two posts first through the link given below
We have already reviewed in detail all the deployment options of the EWM and seen all the steps to connect the Decentralized S/4 HANA EWM or Embedded S4 HANA EWM system to the S4 system having other components like FI, SD, MM etc.
We have already defined Warehouse in S4 (LE Warehouse) in the below post
Now we will define our EWM Warehouse and interface the same to the LE warehouse.
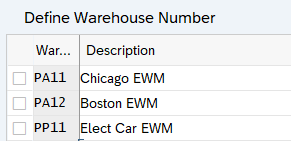
2.1 Define Warehouse Numbers
Here we defines our all three Extended warehouses

We have created below three warehouses for our car business
2.2 Assign Warehouse Numbers
In this step we assign our warehouse number to supply chain unit, Custodian & Default Party to dispose
Note : Please see section 3.3.1.1. for creation of SCU & section 3.3.4 for Party entitled to dispose
Now assign as per the below screenshot

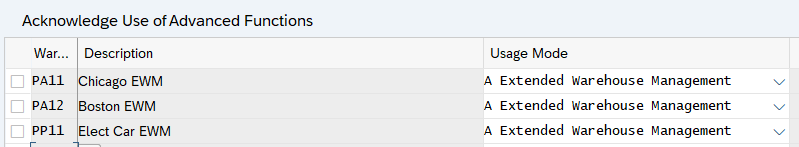
2.3 Acknowledge Use of Advanced Functions
There are two Licence type of EWM
- Basic Warehouse Management
- Extended Warehouse Management
2.3.1 Basic Warehouse Management
In Basic Warehouse Management usage mode, below basic warehousing processes and functions are included
- Inventory Management
- Inbound Processing (for example, Deconsolidation)
- Outbound Processing
- Internal Warehouse Movements
- Physical Inventory
- Reporting
2.3.2 Extended Warehouse Management
In Extended Warehouse Management usage mode, below advanced warehousing functions are included
- Inventory Management Optimization (for example, Slotting)
- Inbound Process Optimization
- Outbound Process Optimization (for example, Waves)
- Material Flow Control
- Yard Management (for example, TU handling, Dock Appointment Scheduling)
- Labor Management
- Value Added Services
- Kitting
- Cross Docking
- Warehouse Billing
- Cartonization Planning
- TM Integration
- IDOC based integration to MFS subsystems

2.4 Map Warehouse Numbers from ERP System to EWM
Here we map the warehouse numbers from SAP S/4HANA or SAP ERP to the warehouse numbers in Extended Warehouse Management (EWM).
2.4.1 In Embedded EWM within S4 HANA
In embedded EWM we can simply assign the 3-digit warehouse number from S4/ERP to the 4-digit EWM warehouse number without specifying any business system
For our car business we assign PA1 to PA11

2.4.2 In Decentralized EWM on S/4 HANA
In decentralized EWM on S4 HANA too, we can simply assign the 3-digit warehouse number from S4/ERP to the 4-digit EWM warehouse number without specifying any business system until we want to create a rule for an exceptional case, where an ERP warehouse should be mapped to a different EWM warehouse number if the data from ERP arrives from a particular business system.
3. Assignment of Organizational units to the EWM warehouse
In this configuration we will configure various EWM organizational unit and assigned them to the EWM warehouse
First we will create supply chain unit of the warehouse
3.1 Supply Chain Unit (SCU)
The supply chain unit is used to model the supply chain of an organization. Supply Chain Unit (SCU) is a physical or organizational unit which has one or more business attributes and used within a logistics process,
SCU has the below characteristics
- Each warehouse number is a unique Supply Chain Unit (SCU) with the Business Attribute INV (Warehouse)
- The supply chain unit contains information, such as country, region, and time zone.
- Time zone of the SCU is used to display all date and time fields for the warehouse.
- SCUs are SCM basis objects and used for structural settings in SAP EWM for
- A warehouse number always has to be connected to a SCU.
- Locations are used for the route determination.
- The plant and the SCUs for the warehouse and shipping points have to be created manually in the decentral EWM & embedded EWM.
3.1.1 Creation of SCU for plant
We will create our plant PA10 as SCU.
SAP Easy Access –> Logistics –>SCM Extended Warehouse Management –>Extended Warehouse Management –>Master Data –>Maintain Supply Chain Unit
T-Code -/SCMB/SCUMAIN


3.1.2 Creation of SCU for Shipping Points
We have the below shipping point assigned to plant PA10 which will be used for deliveries
- PA10 -IC Car Chicago Plant Outbound
- PA20-IC Car Chicago Plant Inbound
Please check the below post for shipping point configuration & assignment
3.1.2.1 Outbound Shipping point SCU


3.1.2.2 Inbound Shipping point SCU

Picture : Creation of SCU for Shipping Points Part 3

3.1.2.3 Supply Chain Hierarchy Maintenance
In a simple warehouse with one shipping & receiving point, the warehouse SCU also has the business attributes SO (shipping office) and RO (receiving office).
T-Code -/SCMB/SCUHIERMAIN

3.2 Custodian
In some industries, especially for logistics service providers, it is common practice to store stocks for more than one plant in the same warehouse number. If you have multiple parties entitled to dispose assigned to the warehouse, you have to assign a custodian to the warehouse number as well. The custodian is the BP that stores, manages, or further processes stock for another BP, but without transfer of title.
- The custodian is usually the owner of the warehouse. The custodian only maintains effective possession of the stock, whereas the owner maintains legal possession.
- The custodian is the owner of the warehouse, whereas the party entitled to dispose is the owner of the stocks. (The custodian may also be referred to as the “holder” of the stocks.).
- To simplify the maintenance, usually the BP of the plant is chosen as the custodian. So, even if the owner of the warehouse is company A, and the plant is called PL01, then you use BP PL01 as the custodian. This saves you the step of creating an additional BP. However, when you use stock for multiple plants within the same warehouse, you can’t do this, and you assign company A as custodian.
3.3 Party Entitled to Dispose
The party entitled to dispose is a BP that represents the party or the organization that is entitled to dispose of the warehouse stock.
Usually, this is the BP of the plant in which the stock is placed and in which the ATP check is performed.
- If you want to manage stocks from several plants in one warehouse, you can use multiple parties entitled to dispose to track the stocks.
- The warehouse-specific product master data in Transaction /SCWM/MAT1 maintains different views per entitled party, this makes it possible to, for example, have a different put-away location determination strategy for different entitled parties, or a different storage process with a value-added service (VAS) step for the goods issue process.
. Every plant BP must have an identification entry with the identification type CRM011, and the identification number that matches the ERP plant. This BP is then one of the available parties entitled to dispose
For each plant in SAP ERP, there is a BP available in EWM. In the standard setup, this BP has the same name as the plant. It can be displayed and maintained in Transaction BP In NW stack it is identified through DB BUT01D IDTYPE "CRM011". But in SAP S/5 stack DB BUT01D is not used and a new dedicated DB table /SCWM/TMAPPLANT is used (View /SCWM/VTMAPPLANT) to assign an entitled to plant
3.3.1 Party Entitle to dispose in Embedded S4 HANA
In Embedded S4 HANA creating of a vendor with plant assigned in enough to declare this BP as party entitled to dispose (& custodian)
Our business partner PA01VEN01 is linked as Supplier to the plant.
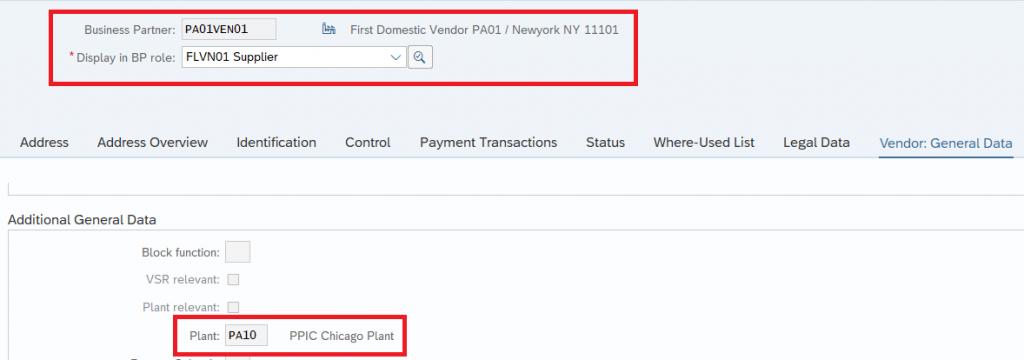
So system will allow BP PA01VEN01 to be given as custodian & Default party to dispose
3.3.2 Party Entitle to dispose in Decentralized S4 HANA
--> In Decentralized S4 HANA in addition to the creating of a vendor with plant assigned to this vendor, We need to assign this BP to the plant in the table /SCWM/TMAPPLANT is used (View /SCWM/VTMAPPLANT)
Below is the path for assignment of a disposal party to a plant
SPRO –> SCM Extended Warehouse Management –> Interfaces –> ERP Integration –> General Settings –> Assign Business Partners to Plant

4. Assignment of EWM stock types & availability group to the S4 Plants and SLOCs.
Here we the map storage locations to the EWM warehouse numbers in and assign an availability group to each storage location.
--> if We want to have separate visibility of the stock which is still under put away to the stock which is completely available then we will map separate storage locations to the respective availability groups --> if We want to have separate visibility of the stock for a particular process (for example-spare parts) which is still under put away to the stock which is completely available then we will map additional separate storage locations created especially for the process (for example-spares) to the respective availability groups
Here we define the availability groups of the warehouse, their relationship to the stock types and, optionally, to the storage types.
In a warehouse linked to one plant and one storage location, you define one availability group, which represents the plant and storage location, and assign it to all stock types of the warehouse.
Note: If you keep stock in the goods receipt zone separate from stock on final bins in terms of ATP availability, you define two availability groups, each representing one storage location. You assign each availability group to a set of stock types. In the goods receipt zone, you manage stock in stock types of one availability group. In final storage types, you manage stock in stock types of the other availability group. When you confirm put-away warehouse tasks, the system automatically posts the stock from the stock type of one availability group to the corresponding stock type of the other availability group.
4.1 Configure Availability Groups
First, we will configure availability groups.
We will configure availability group separately for --> 1)-Availability groups for raw, semi-finished & finished materials, --> 2)-Availability groups for Production staging materials --> 3)-Availability groups for spare parts.
4.1 Configure Availability Group for Put-away for Raw, Semi-finish & Finished Materials
Below is the path to configure availability Group for Put-away for Raw, Semi-finish & Finished Materials

In our EWM we have configured two main availability groups, 001 for goods in put-away and 002 for goods available for sale. This is assigned to the plant and storage location of the EWM warehouse in SAP S/4HANA

4.2 Configure Availability Group for Put-away for Production Materials
Since we want to keep stock in production supply areas separate from stock on final bins, we will define a separate availability group, a set of stock types, and a storage location for the production supply areas.

Picture: Availability Group for Put-away for Production Materials
4.3 Configure Availability Group for Put-away for Spare Parts
Since we want to keep stock of spare parts separate from other materials stock on final bins, we will define a separate availability group, a set of stock types, and a storage location for the production supply areas.

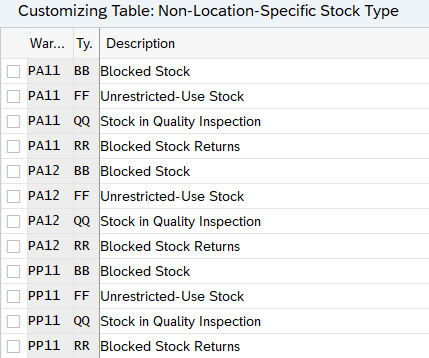
4.2 Define Non-Location-Dependent Stock Type
These are stock types that group stock based on their attributes and are independent of stock location in the warehouse. SAP has provided some non-location-specific stock types by default, but we can create more per our business requirements.
4.3 Configure Stock Type
In this activity, map the availability group and non-location-specific stock type with the stock type in embedded EWM for a specific warehouse like F1-UNR Stock in Put-away, F2-UNR Stock Warehouse. Now this EWM stock type is mapped to non-location specific stock type and availability group F1(UNR Stock in Put-away) is mapped to 001 (Goods in put-away) & FF (UNR Use-Stock) F2 (UNR Stock in WH) is mapped to 002 (Goods Completely Available)
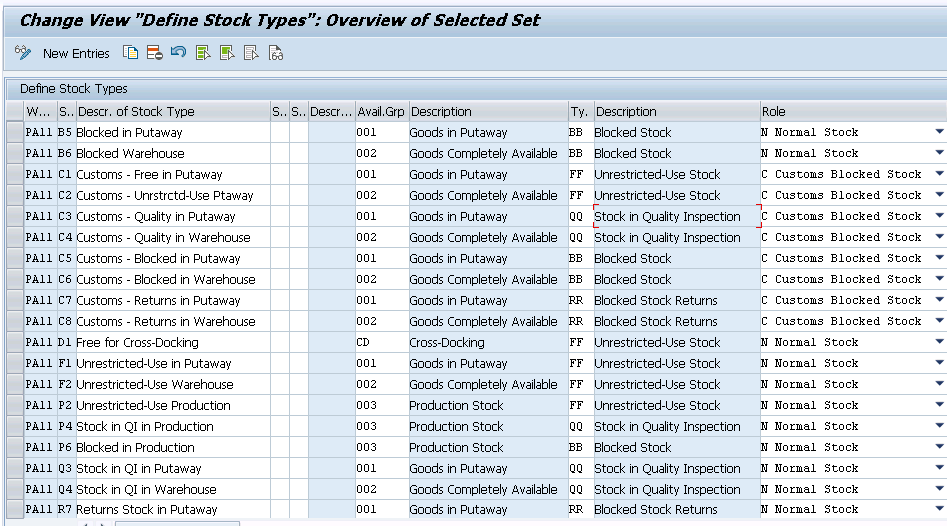

4.4 Map Storage Locations from ERP/S4 System to EWM
Here we map storage locations onto the warehouse numbers in Extended Warehouse Management (EWM) and assign an availability group to each storage location.


Note: We have created the plant vendor PA01VEN01 and assigned the same to as “Default party for disposal” for warehouses PA11
4.5 How Availability Works in EWM
When an inbound delivery is created in embedded EWM,
- The system checks the plant and storage location for the delivery in SAP S/4HANA and determines the availability group for that plant and storage location combination. So here for SLOC PP1D, availability group is determined as 001 (Goods in put-away).
- Next, it determines the embedded EWM stock type by looking at the mapping of the availability group and non-location-specific stock type based on the stock category for the delivery in SAP S/4HANA (which is UNR so non location stock is FF (UNR Use-Stock) and determines the embedded EWM stock type as F1(UNR Stock in Put-away).
- This stock type is populated in the inbound delivery created in embedded EWM, so in IBD EWM stock type F1 is populated.
HINT
You can also assign an availability group to storage types in storage type settings. If the availability group of stock being put away into a storage bin for the storage type is different from the availability group set in the storage type, then the system does a posting change for the stock. For example, if stock in the delivery with stock type Fl, is put away in a storage type with availability group 002, then based on the settings discussed previously availability group 002 mapped to stock type F2- the system will perform a posting change on stock being put away and change it to type F2, which is unrestricted stock available for sale. This in turn post a storage location change in S4 HANA to the corresponding SLOC “PP1S”
Note
Availability group is also set at the WPT level. The system always gives preference to the availability group set at the storage type level, if it doesn’t find one, it looks for an availability group set at the process type level. If no availability group is set at either of these levels, then the embedded EWM stock type remains unchanged.
5. Warehouse-dependent Number Ranges
Define Number Ranges for the following:
◦Warehouse tasks or warehouse documents
◦Waves
◦Warehouse orders
◦Consolidation groups
• Define Number Range for Physical Inventory Documents
• Define Number Range for HU Identification
5.1 Define Warehouse Number Control
Here you define the basic data for a warehouse number. For example, weight, volume, time & length units, Default Storage Process Types for special activities, Determination Procedure for Condition Technique etc

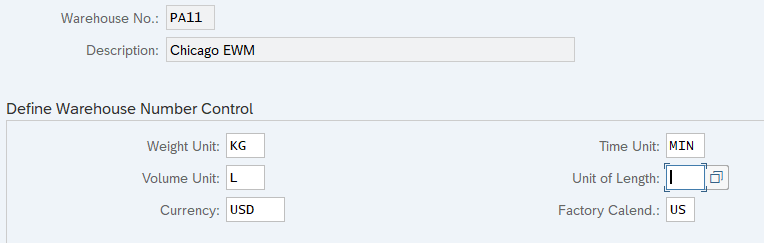
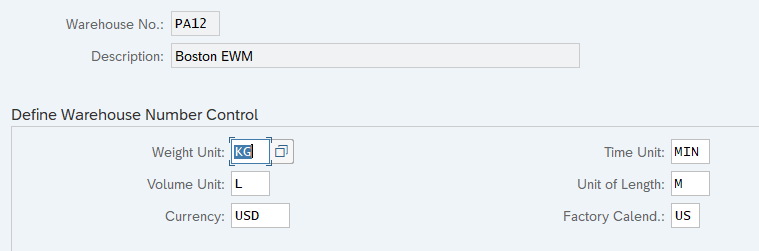
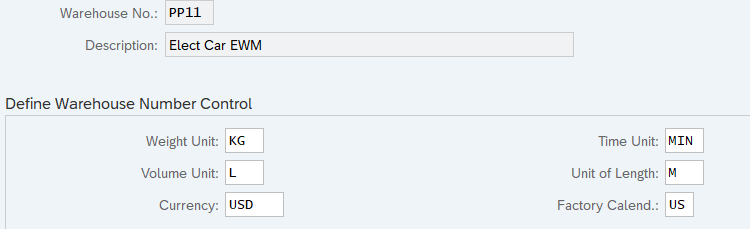
5. Delivery Document Integration configuration
Here we configure the mapping of ERP-EWM delivery document types, item types etc.
Please refer the below post for step by step configuration of inbound delivery & outbound delivery document integration components.
6. Extra Steps for Decentralized EWM on S4 HANA
For Decentralized EWM on S4 we need to perform the below extra configurations.
6.1 Set Control Parameters for ERP Version Control
Below are the parameters to be configured here
6.1.1 SAP Release
It should be “S4_OP_100 for all SAP S4/HANA 1610 & Higher
6.1.2 Inbound Delivery Related Settings
Below are the settings needs to be performed related to the inbound delivery.
6.1.2.1 General Settings
Below is the inbound delivery related general settings
6.1.2.1.1 Unique ASN Number
We will not check if A|SN number is unique so set it to “Do not check if ASN Number is Unique”
6.1.2.1.2 Perform Inbound Delivery Split
We will split the inbound delivery so choose “Perform Inbound Delivery Split & Report to ERP”
6.1.2.1.3 Report in Yard to ERP
Choose “Report in Yard to ERP”
6.1.2.1.4 Confirmation Type of SNs
Only serial numbers to be reported to ERP where goods movement is posted so choose “Only Communicate Goods Movement Posted Serial Numbers”.
6.1.2.2 Goods Movement Related Settings
Below are the goods movement related settings
6.1.2.2.1 Goods Receipt Mode
There are four options here
- Immediately Send GR Posting and Partial GR Posting to ERP
- Only send Full GR at end of Put away process
- Send Full GR when GR has been posted for all items
- Send Collective GR
Select “Immediately Send GR Posting and Partial GR Posting to ERP” here.
6.1.2.2.2 Posting Change with Reference to an Inbound Delivery
Choose the option of ” Post.Chg.in ERP can Be Posted wrt Inb. Deliv.” The other option is -cannot be posted wrt. inbound delivery
6.1.2.2.3 Sequence of Post. Chg. And GR Messages
Choose the option of “Send Post. Chg. Message Before Full GR Message”. The other available option is “Send Post. Chg. Message After Full GR Message”
6.1.2.3 Quality Inspection Related Settings
Below are the goods movement related settings
6.1.2.3.1 Possible Usage Decisions
Three available options here
- All Inspection Decisions Can Be Made
- Internal Inspection Decision and stock transfer
- No external Inspection Decisions
Choose option “All Inspection Decisions Can Be Made” here
6.1.2.3.2 Quality Confirmation for Returns
Choose the option of “Quality Confirmation for Returns”. The other option available is “Do not Communicate Inspection Results to ERP”
6.1.2.3.3 Quality Management Integration
Choose option “Quality Management with QIE or Integrated in ERP QM”. The other available option is “Quality management Only in EWM (QIE)”
6.1.2.4 Batch Control Related Settings
Below are the batch control related settings
6.1.2.4.1 Prevent Batch Creation in EWM
We will receive batch from S4. So, choose option “Batch Creation Forbidden in EWM”. The other option is “Batch Creation Allowed in EWM”
6.1.2.4.2 Batch Update
This is not relevant now due to above option of “Batch Creation Forbidden in EWM”
6.1.2.4.3 Batch Change in Inbound Delivery
Choose option of “Batch change not allowed”. The other option is “Batch Can be Changed Using External Logic”
6.1.2.4.4 Communication of Batch Split of IDL Item
Choose option of ” Immediately Communicate Batch Split when Saving Delivery “. The other option is “”Only communicate batch split at Goods Receipt”
6.1.2.4.5 Report Batch Changes to ERP
Choose option of ” Send Batch Change Immediately to ERP via REPLACE “. The other option is “”Only send batch change to ERP at Goods Receipt”
6.1.2.5 Create/Delete Inbound Deliveries Related Settings
In this section we will do settings related to the creation and deletion of inbound deliveries in decentralized S4 HANA.
6.1.2.5.1 Create Inbound Delivery in EWM
Choose the option of “Possible to Locally Create Inbound Delivery in EWM”
The other available options are
- Not possible to Locally Create Inbound Delivery in EWM
- Local Creation possible, Except by production
- Local creation from template possible
6.1.2.5.2 Create Inbound Delivery Item in EWM
Choose the option of “Inbound Delivery Item Can Be Created Locally in EWM”
The other available options are
- Inbound Delivery Item Cannot Be Created Locally in EWM
- Local creation from template possible
6.1.2.5.3 Delete Inbound Delivery
Choose option of Can be deleted. The other option is “IBD cannot be deleted”
6.1.2.5.4 Delete Inbound Delivery Item
Choose option of Can be deleted. The other option is “IBD item cannot be deleted”
6.1.2.5.5 Create Inb. Del. For a Plant as a Vendor
Choose creation of IBD allowed. The other option is IBD creation not allowed
6.1.3 Outbound Delivery Related Settings
Below are the settings related to the outbound deliveries.
6.1.3.1 Check for Kit Header Item in HU at Goods Issue
Choose “Carry Out Kit Check”. The other option is do not carry out kit check.
6.1.3.2 Cross-Delivery HUs
Choose the option of “Normal Creation and Communication of Cross-HUs”. The other available option is “Do-not Communicate Cross-HUs to ERP”
6.1.3.3 Perform Goods Issue Cancellation
Choose option “Cancel Goods issue”. The opter option is “Do not cancel Goods issue”
6.1.3.4 Invoice Creation Before GI
Choose ” Possible to Create Invoice Before Goods Issue”.
The other options are
- Generally, not Possible to Create Invoice Before Goods Issue
- Not Possible to Create Invoice Before Goods Issue for ERP
- Not Possible to Create Invoice Before Goods Issue for CRM
6.1.3.5 Delete Outbound Delivery
Choose option “Outbound Delivery Can Be Deleted”. The opter option is “Outbound Delivery Cannot Be Deleted”
6.1.3.6 Pick Denial Message to ERP
Choose option “Send Pick Denial Message to ERP”. The opter option is “Do not Send Pick Denial Message to ERP”
6.1.3.7 Communication of Batch Split of OD Item
Choose option “Immediately Communicate Batch Split when Saving Delivery”.
The opter available options are
- Only Communicate Batch Split at Goods Issue
- Only Communicate Batch change at Goods Issue
- Immediately Communicate Batch Split quantity change
6.1.3.8 Split Reversal
Choose option “Split Reversal Allowed”. The opter option is “Split Reversal not Allowed”
6.1.3.9 Distr. Of Direct Outbound Deliveries
Choose option “Outb. Delivs. Can Be Created Locally and Distributed to ERP”. The opter option is “Outb. Delivs. Cannot Be Created Locally”
6.1.3.10 Communication of UoM Split
Choose option “Communicate UoM Splits”. The opter option is “Do not Communicate UoM Splits”
6.1.3.11 Goods Issue from Consignment Stock
Choose option “Transfer Stock to Own Stock Before Posting Goods Issue”. The opter option is “Post Goods Issue from Consignment Stock”
6.1.4 non-Delivery based Settings
Below are the settings related to the non-delivery
6.1.4.1 Stock comparison Type
Choose option “Synchronous stock comparison”. The opter option is “Asynchronous stock comparison using IDOCs”
6.1.4.2 Communicate Alternate UoM to GM Intf.
Choose option “Communicate Alternative UoM”. The opter option is “Communicate Basic UoM”
Control Parameters for ERP Version Control are completed now.
7. Cross Landscape Distribution (XLD) for Decentralized S4 HANA EWM
If we are working with decentralized EWM on S4 HANA option, then it is very critical to keep S4 & decentralized EWM systems in sync.
XLD ensured that SAP ERP and EWM Customizing are always in Synchronization --> We can compare the entries between the decentralized EWM and S/4HANA through the SCMP and make both systems in synch through manual configuration. --> Alternatively, Cross-landscape system transports (“XLD” transports) can be set up through Solution Manager to automate the distribution of configuration entries between S/4HANA and decentralized EWM for a selected set of tables.
Below is the list of fields/tables which are necessary to be in sync between S4 HANA & Decentralized EWM on S4 HANA.




Note: You can download the SAP authorized guide from where the above list of fields is taken.
Integration of SAP ERP or SAP S/4HANA with
decentralized EWM in SAP S/4HANA
Business photo created by freepik – www.freepik.com
In the previous post we have configured Initial settings in ERP/S4 which are necessary to run the EWM system for Embedded as well as decentralized EWM. Please click on the above link to see the details.
In the next post we will configure EWM Storage Type. Please click on the above link to see the details.






