How to Configure SAP S4 HANA Sales Pricing
- Step 1-Understand SAP S4 HANA Sales Pricing
Explaining of the main components of SAP S4 HANA Sales Pricing
- Step 2-Define Pricing Procedure
Defining the Pricing Procedure for all scenarios like -Standard Sales Order, Standard Billing, Inter-Company STO Billing etc.
- Step 3-Determine Pricing Procedure
Here we have explained all the Component of Pricing Procedure Determination like : Customer Pricing Procedure, Document Pricing Procedure etc.
Table of Contents
1. What is SAP S4 HANA Sales Pricing
A SAP S4 HANA Sales Pricing in SAP SD (Sales and Distribution) determines how the system calculates the price of a product or service during the sales process.
--> SAP S4 HANA Sales Pricing defines a sequence of pricing conditions like base price, discounts, taxes, and surcharges, ensuring accurate pricing for customers.
--> Each sales document (sales order, invoice etc.) uses a specific pricing procedure.
Thus SAP S4 HANA Sales Pricing streamlines price determination in sales. It ensures compliance with business rules and legal requirements in sales transactions.
1.1 Main Components of SAP S4 HANA Sales Pricing
The main components of SAP S4 HANA Sales Pricing Procedure are given below
- Condition Types: Represent specific pricing elements like base price, discounts, surcharges, and taxes (e.g., PR00 for price, K007 for discount).
- Access Sequence: Determines the order in which the system searches for valid condition records for a condition type.
- Condition Tables: Store pricing data, such as customer-specific or material-specific prices.
- Pricing Procedure: A defined sequence of condition types that the system follows to calculate the final price in a sales document.
- Condition Records: Actual data (e.g., price, discount rates) stored in condition tables.
We will explain all the main components of SAP S4 HANA Sales Pricing.
1.1.1 Condition Types
Condition types represents components of total price such as price, discounts, surcharges & taxes etc..
We will configure a very simple pricing procedure to understand the things better. We will include below condition Types in our customized pricing procedure --> PR00 (Gross Price) --> SAP Standard --> Y007 (Customer Discount) --> Copy from Std K007 --> Y005 (Disc.Customer/Material) --> Copy from Std K005 --> YB00 (Discount (Value)) --Copy from Std RB00 --> YF00 (Freight) --Copy from Std KF00 --> YD00 (Freight) --Copy from Std HD00 --> UTXJ (Tax Jurisdict.Code) --> SAP Standard --> JR1 (Tax Jur Code Level 1) --> JR2 (Tax Jur Code Level 2) --> JR3 (Tax Jur Code Level 3) --> VPRS (Internal price) --> SAP Standard
We will review each field used in the condition types configuration through configuration of gross price condition type PPR0
To configure the condition types follow the below path
SPRO –> Sales and Distribution –> Basic Functions –> Pricing –> Pricing Control –> Define Condition Types
Alternatively you can run transaction code V/06
Important fields in Condition Type configuration and their explanation
1.1.1.1 Main Pricing Condition Type PPR0
For our pricing procedure base price, we will use SAP standard PPR0 condition type.
The PPR0 pricing condition in SAP SD is the standard condition type used to represent the base price of a material or service in a sales transaction.
PPR0 pricing condition is the starting point for pricing calculations, and other conditions like discounts, surcharges, or taxes are applied on top of it.
--> The PPR0 condition ensures that the correct base price is pulled into the sales order from condition records, forming the foundation for the final price determination.
a) Fields in the Main Header Screen
Below are the fields.

1. Condition Type
Here we give the 4 characters code & description of our condition type. For example -here SAP have used code as “PPR0” & description as “Price” for the default gross price condition type.
2. Access sequence
Every condition type is associated with one access sequence that access sequence should be assign here. for our condition type PPR0, access sequence is used as “PPR0”
b) Fields in the “Control Data 1” Sub-screen
Below fields are present in this sub-screen
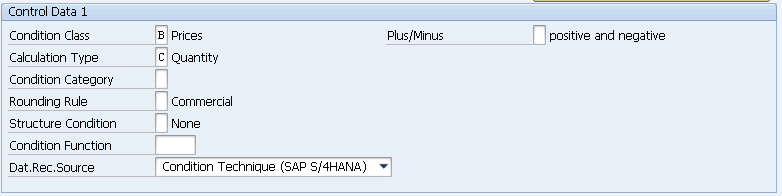
1. Condition Class
It is a classification of condition types as prices, taxes, discounts, etc.
2. Calculation Type
This field decides how calculation should be done for this condition like-quantity or percentage or fixed amount.
3. Condition Category
A classification of conditions according to predefined categories. For example-Freight.
4. Rounding Rule
Round up or round down can be assigned.
5. Structure Condition
The condition type is used in BOM or configurable material.
6. Plus/Minus
This field determines the value of the condition type should be added or deducted.
c) Fields in the “Group Condition” Sub-screen
Below are the main fields in the “Group Condition” Sub-screen

1) Group Condition
It indicates whether the system calculates the basis for the scale value for more than one item in a document.
d) Fields in the “Changes which can be made” Sub-screen
Below are the main fields in the “Changes which can be made” Sub-screen.
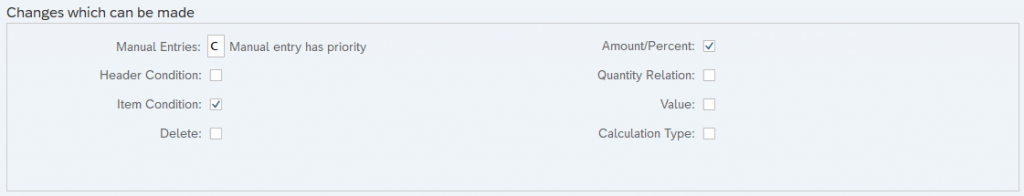
1. Manual Entries
The value of this field determines whether the condition type is determined manually or not at sales order level
2. Header Condition
The value of the header condition applies to whole items in the sales order. Header conditions do not have any access sequence. The values should be entered manually in the sales order level.
3. Check Item Condition
The value of the item condition applies to only at item level. Item conditions must have access sequence.
4. Delete
This indicator enables to delete the condition type at sales order level.
5. Amount/Percentage
It specifies whether the amount or percentage for the condition type can be changed during document processing. These changes will not affect the condition master data.
6. Value
Scope for changing the value. It specifies whether the value of the condition type can be changed during document processing.
7. Quantity Relation
It specifies the scope of changing conversion factors during document processing.
8. Calculation Type
If you want to change calculation type this indicator should be set. For Example-Normal calculation type is fixed amount and sales order level calculation type is percentage.
e) Fields in the “Master Data” Sub-screen
Below are the main fields in the “Master Data” Sub-screen
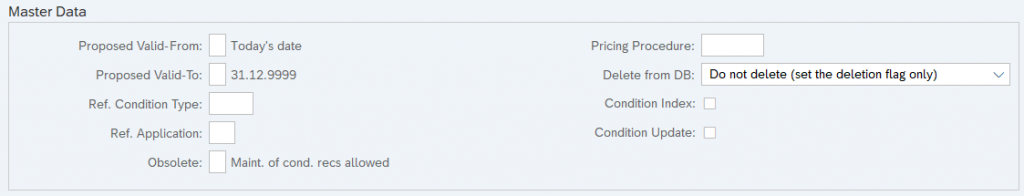
1. Valid From
It specifies the beginning validity date that the system automatically proposes when we create a rebate agreement of this type. It is most relevant for condition type B001, B002, and B003.
2. Valid To
The proposed value for how long a condition should remain valid.
3. Reference Condition Type
In our pricing procedure if we have SAME condition types, then we can maintain condition records for one condition type and we can specify another condition type as a reference condition type for this condition type. So that, no need to create condition records for reference condition types.
4. Reference Application
If we reference one condition type for another condition type, we should specify in which application area this referencing procedure takes place.
5. Pricing Procedure Condition Supplement
When the business wants to give certain discounts for all the customers and materials till certain period.
6. Deletion from Database
We can set system responses when the condition record is going to be deleted from the database like with popup or without popup messages.
7. Check Condition index
We can create condition index for this condition type. So that by using the condition index we can maintain the condition records of this condition type.
8. Condition update
This field is for qualifies condition index. This indicator updates the condition type. For example “By value”.
f) Fields in the “Scales” Sub-screen
Below are the main fields in the “Scales” Sub-screen
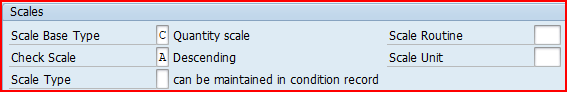
1. Scale Basis
Depending upon the range of quantity prices may be increased or decreased, higher discounts, low freight charges can be offered.
2. Check Value
We can specify the checking rule for scale rates as a ascending or descending.
3. Scale Type
The indicator controls the validity of the scale value or percentage from a certain quantity or a value. Alternatively it is possible to work with interval scales that must be stored in the condition type.
4. Scale Formula
We can specify the formula for determining the scale base value which may has not been provided in the standard system.
5. Unit of Measure
System uses unit of measure to determine scales when we use group conditions.
g) Fields in the “Control Data 2” Sub-screen
Below are the main fields in the “Control Data 2” Sub-screen.
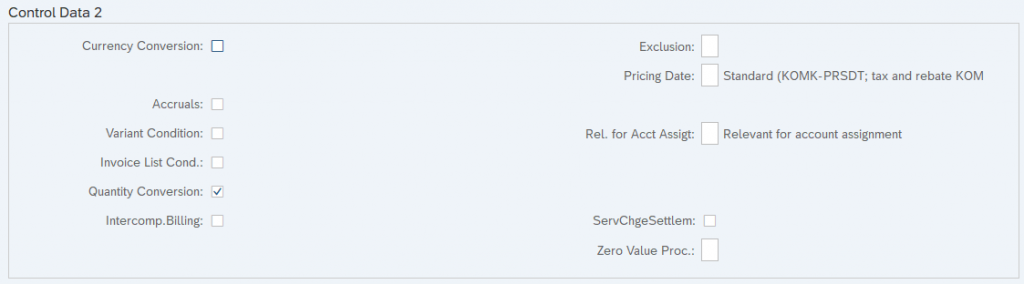
1. Currency Conversion
It controls the currency conversion where the currency in the condition record varies with document currency.
2. Accruals
It indicates that the system posts the amount resulting from this condition to the financial accounting as a accruals. If you mark this field the condition appears in the document as a statistical value.
3. Invoice list Condition
Indicates If the condition type is relevant for internal costing.
4. Inter-Company Billing Condition
Indicates If the condition type is inter-company billing purpose, Ex-PI01.
5. Service Charge Settlement
It indicates that the trading contract conditions should be calculated using vendor billing document.
6. Variant Condition
Indicates If the condition type is for variant pricing [Variant configuration], Ex-VA00.
7. Quantity Conversion
This field controls the quantity conversion during determination of the condition bases. This field only relevant for quantity dependent condition types. If you deactivated it, then the condition bases quantity is converted via the quantity to the stock-keeping unit.
8. Exclusion
We can offer best condition type among the same conditions to the customer by using “condition exclusion” feature.
9. Pricing Date
We can specify the pricing date at which this condition to be affected.
10. Relevant for Account Assignment
Indicates whether this condition type is relevant for account assignment or not. It is the main control to post the values of condition type into the respective G/L accounts.
11. Service Charge Settlement (Trading Contract)
Indicates that the trading contract conditions should be calculated using the supplier billing document.
12. Process conditions with value equal to zero
Using this indicator, you can control how conditions with value equal to zero are processed.
If left blank -Conditions are not considered in the condition exclusion logic when their value is equal to zero.
If set to “A”-Conditions of this type will be considered in the exclusion logic even if their value is equal to zero.
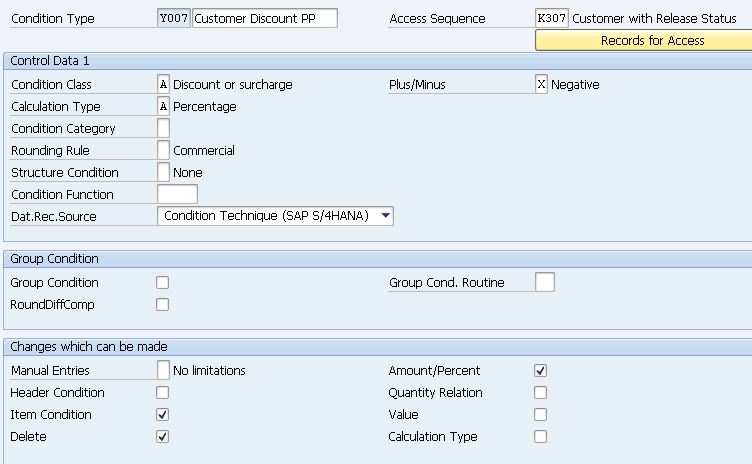
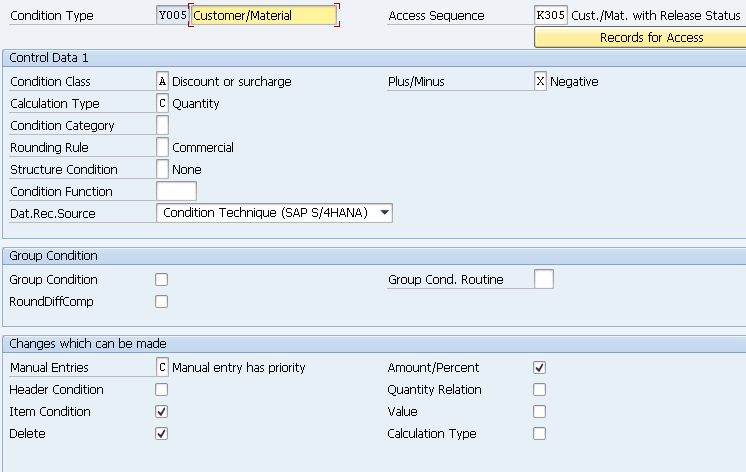
1.1.1.2 Discount Condition Types
We are creating three condition types for discounts as given below
- Y007 (Customer Discount) –> Copy from Std K007
- Y005 (Disc.Customer/Material) –> Copy from Std K005 –>
- YB00 (Discount (Value)) –Copy from Std RB00
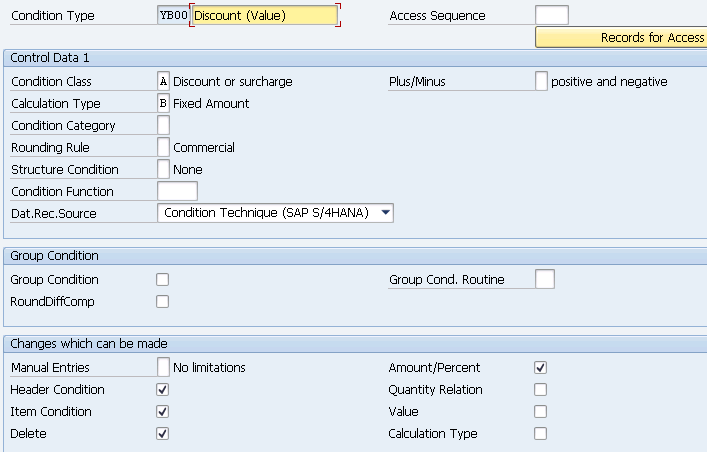
1.1.1.3 Freight Condition Types
We are creating two condition types for discounts as given below
- YF00 (Freight) –Copy from Std KF00
- YD00 (Freight) –Copy from Std HD00
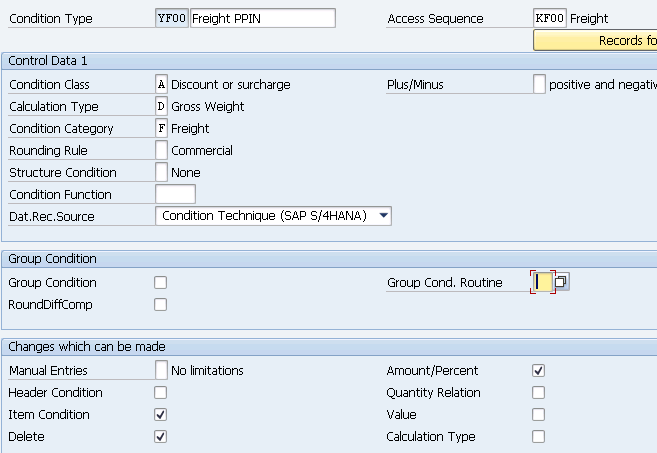
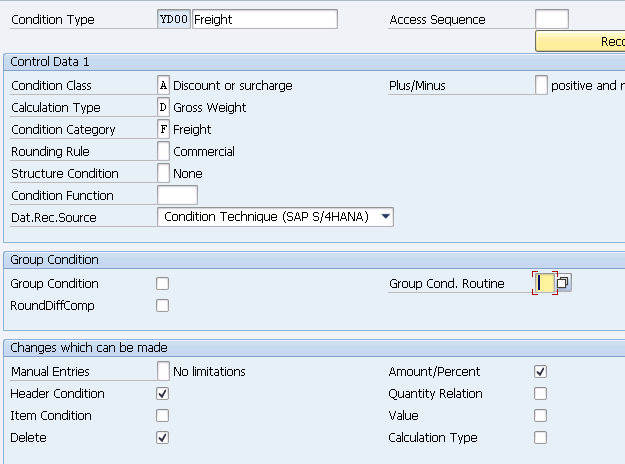
2. Define Pricing Procedure
Pricing procedure is a list of condition types in a specific order, such as gross price less discount & plus tax to arrive on net price.
The pricing procedure fulfills the need of business like correct pricing, discounting, adherence to tax laws etc.
We will configure a customized Pricing Procedure “PPIN01- PPN Pricing Procedure” for our car business.
As described in the condition type topic we will use below customized condition types to build our customized pricing procedure.
--> PR00 (Gross Price) --> Y007 (Customer Discount) --> Y005 (Disc.Customer/Material) --> YB00 (Discount (Value)) --> YF00 (Freight) --> YD00 (Freight) --> UTXJ (Output Tax) --> JR1 (Tax Jur Code Level 1) --> JR2 (Tax Jur Code Level 2) --> JR3 (Tax Jur Code Level 3) --> VPRS (Internal price)
We have configured the pricing procedure in the system
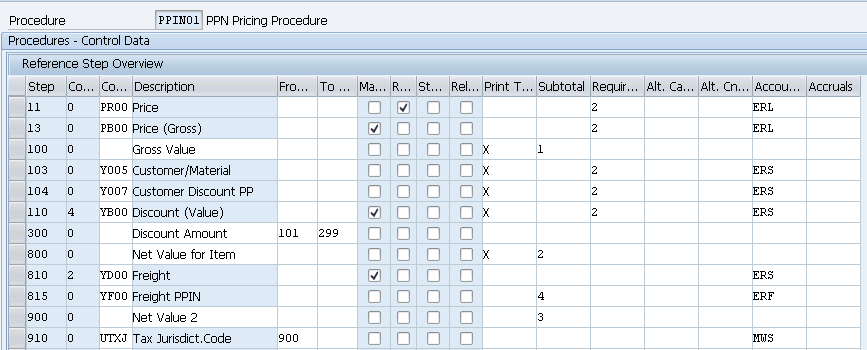
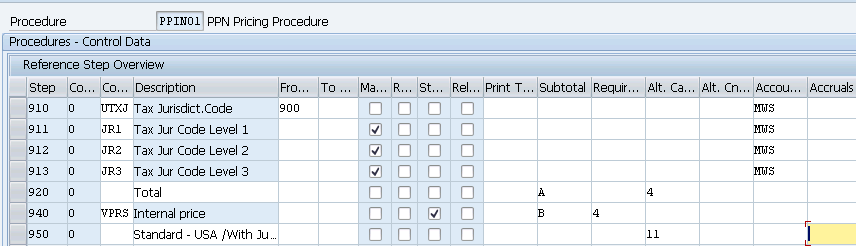
We will Configure now Important fields in Pricing procedure configuration and their explanation
2.1 Important Field in Pricing Procedure
Below are the Important fields in Pricing procedure configuration and their explanation
a) Step
Indicates the step number of condition type in pricing procedure like 10, 20, 30, and etc. If we give steps intervals of 1, but this can make changing the procedure in the future very difficult.
b) Counter
System uses the counter while accessing the condition types in our pricing procedure. This is used to show a second mini – step within an actual step.
c) Condition type
We specify condition types (pricing elements) that are participating to calculate net value in our pricing procedure.
d) Description
System copies the description of the condition type from definition of condition type.
e) “From Step” and “To Step”
As a base to calculate further value of condition type. We can specify the base for condition type. So that system takes the base (step).
f) Manual
It determines if condition type is determined in our pricing procedure manually.
g) Mandatory
indicates that the particular condition type is mandatory in pricing procedure.
h) Statistical
It indicates the purpose of condition type is only for information purpose. The value of condition type will not be taken into consideration in the net value calculation.
i) Print
It indicates the value of the condition type can be printed in a document.
j) Sub – total
The value of this field determines where the value of the sub – totals is going to be stored in the database.
k) Requirement
Requirement is used for condition type that excludes particular condition type while determining the net value. Example -PR00 pricing condition type is not necessary for items not relevant for pricing. We assign requirement 002 to the requirement column fulfil this.
l) Alternative formula for calculation type
Indicates alternative formula instead of standard one as a condition type in the form of routines. Example : Routine 11 profit margins can be used as a alternative formula for condition type to calculate profit margin as there is no standard condition type to calculate profit margin.
m) Alternative formula for condition base value
Here we can use a formula in the form of routine to use base. Example-routine 12 or 13 (gross weight or net weight) can be used with condition type KF00 to calculate fright.
n) Accounting keys and accruals
The values of the pricing elements (condition types) can be posted in the respective G/L accounts through this accounting keys.
2.2 Pricing Procedure for Standard Sales
For the standard sales order we use SAP standard pricing procedure as explained HERE
2.3 Pricing Procedure for Inter-Company STO Billing
for Inter-company STO Process with Delivery & Billing, we have used SAP Standard billing pricing procedure “A17J11 – IC Stock Transfer (US)”
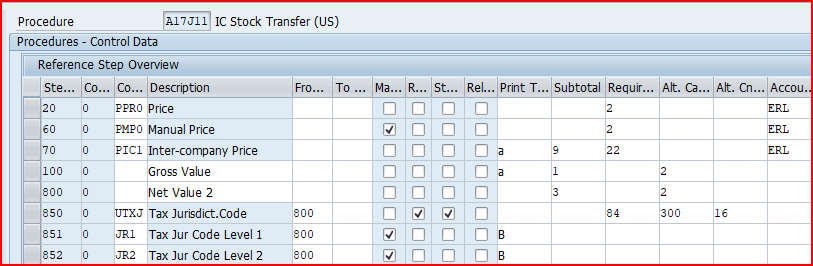
3. Determination of Pricing Procedure
S4 HANA Sales Pricing procedure is determined based on the below components
- Sales Area (Sales Organization, Distribution Channel & Division) of the selling company
- Customer Pricing Procedure – This is inputted in the BP Customer master data
- Document Pricing Procedure – It is assigned to the sales document type i.e. Sales order types , Billing types etc.
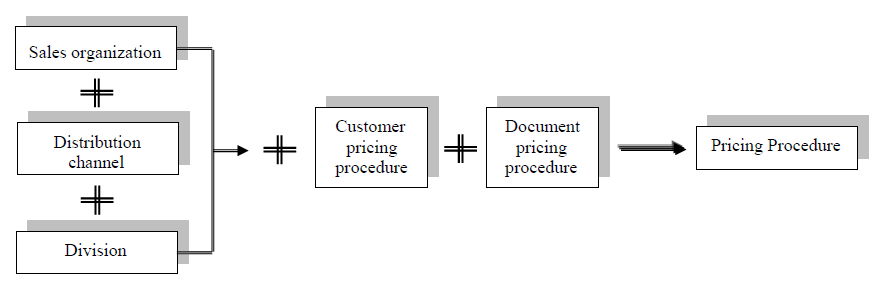
We will configure the pricing procedure determination for all scenarios
3.1 Pricing Procedure Determination for Standard Sales Order
We will first configure all the necessary components for Pricing Procedure Determination for Standard Sales Order
3.1.1 Customer Pricing Procedures
You specify the customer pricing procedure in the customer master record for each sales area
SPRO –> Sales and Distribution –> Basic Functions –> Pricing Control –>Define And Assign Pricing Procedures –> Set Customer Pricing Procedures
3.1.2 Document Pricing Procedure
Follow the below path to configure Document Pricing Procedure
SPRO –> Sales and Distribution –> Basic Functions –> Pricing Control –>Define And Assign Pricing Procedures –> Set Document Pricing Procedures
You specify the document pricing procedure for each sales document type and billing type.
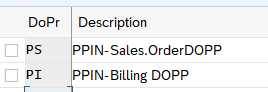
3.1.3 Assign Document Pricing Procedure to Sales Order type
Follow the below path to Assign Document Pricing Procedure to Sales Order type.
SPRO –> Sales and Distribution –> Basic Functions –> Pricing Control –>Define And Assign Pricing Procedures –> Assign Document Pricing Procedures to Order Types
We have configured our own Order type “YOR”
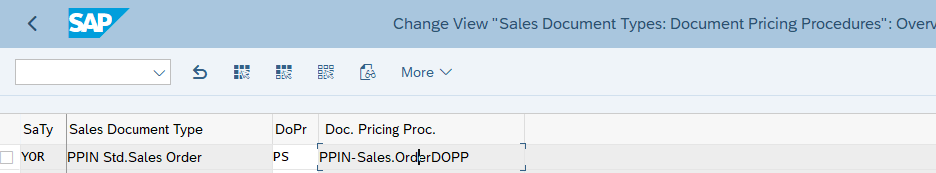
Please see the below post to check the configuration of sales document type “YOR”
Configure SAP S4 HANA Sales Documents in 10 Minutes – Sales Order Type Configuration
3.1.4 Assign Document Pricing Procedure to Billing type
Follow the below path to Assign Document Pricing Procedure to Billing type.
SPRO –> Sales and Distribution –> Basic Functions –> Pricing Control –>Define And Assign Pricing Procedures –> Assign Document Pricing Procedures to Billing Types
Assign the configure document pricing procedure to our own standard billing type “YF2”
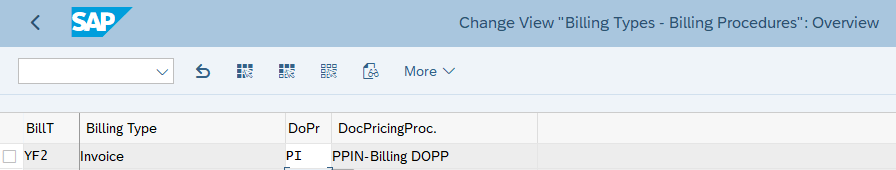
Please see the below post to check the configuration of billing type “YF2”
Master SAP SD Billing Configuration – Billing Type for Standard Sales Order
3.1.5 Assign Pricing Procedure
Now we will assign pricing procedure to our standard sales scenario . We have already defined our pricing procedure for standard order HERE
To assign the pricing procedure follow the below path
SPRO –> Sales and Distribution –> Basic Functions –> Pricing –> Pricing Control –>Define And Assign Pricing Procedures –> Set Pricing Procedure Determination
Alternatively use transaction code OVKK
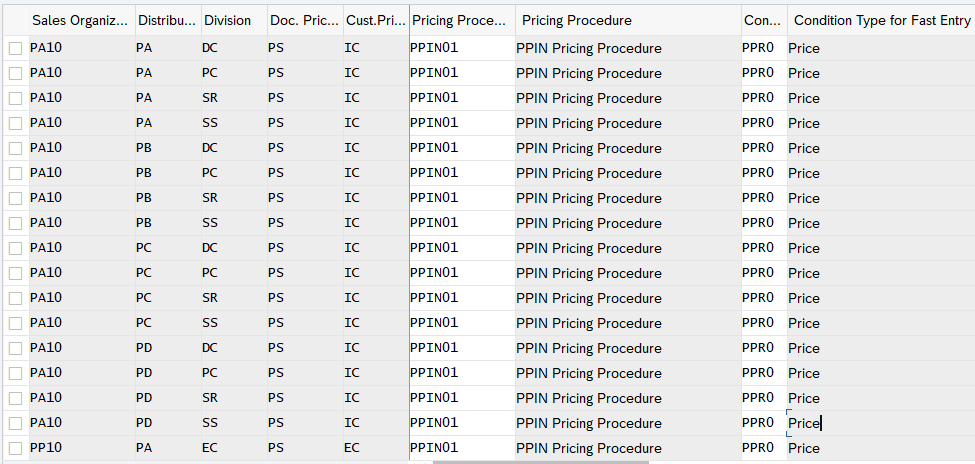
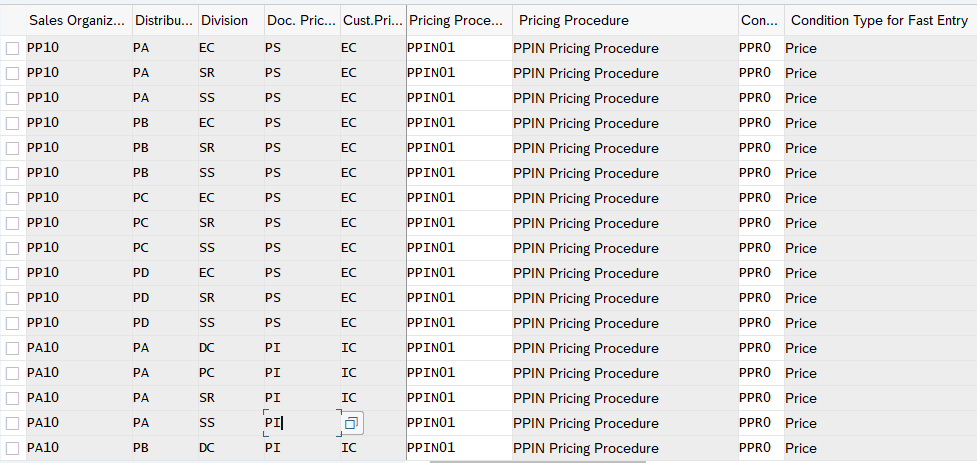
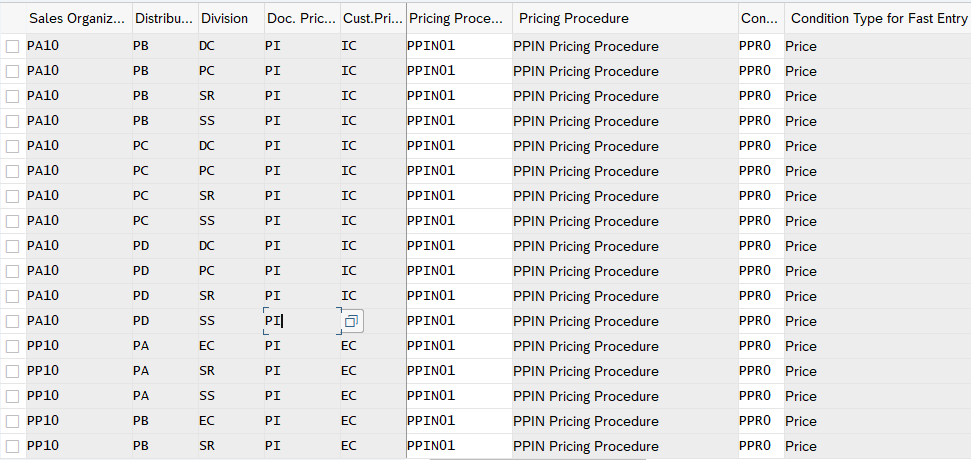
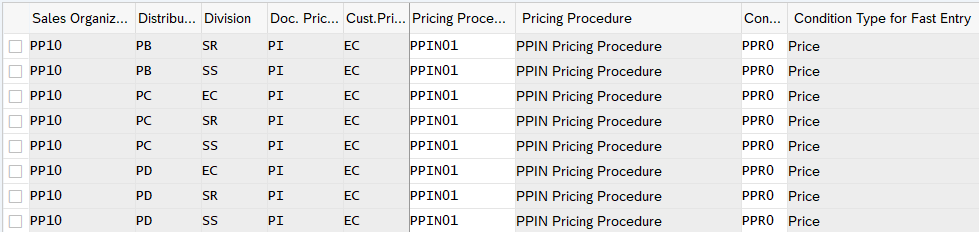
3.2 Pricing Procedure Determination for Inter-Company STO Billing
We will configure all the necessary components to determine the above pricing procedure for Inter-Company STO Billing
3.2.1 Customer Pricing Procedures
You specify the customer pricing procedure in the customer master record for each sales area
for IC STO Billing we have configured Customer Pricing Procedure as “02”-IC STO DLv Bill Proc
SPRO –> Sales and Distribution –> Basic Functions –> Pricing Control –>Define And Assign Pricing Procedures –> Set Customer Pricing Procedures
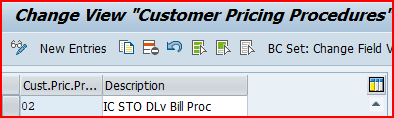
Note: We assign this “Customer Pricing Procedure” to the BP Customer for Inter-Company STO with Delivery & Billing.
Please see the below post for detail
How To Configure S4HANA BP and CVI In 7 Easy Steps – Creation of BP Customer for Inter-Company STO with Delivery & Billing
3.2.2 Document Pricing Procedure
SPRO –> Sales and Distribution –> Basic Functions –> Pricing Control –>Define And Assign Pricing Procedures –> Set Document Pricing Procedures
For the scenario “IC STO with Delivery & Billing”, we have used document Pricing Procedure as “ST-IC Stock Transfer”
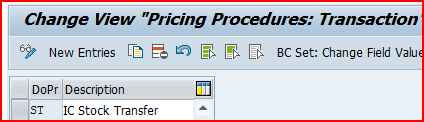
3.2.3 Assign Document Pricing Procedure to PO type
In Inter-Company STO, the document type is PO (STO).
So here we assign the pricing procedure to STO document type in Material Management
Ultimate guide to SAP S4 HANA MM Pricing Procedure – Define Schema Determination for Inter-company STO Process with Delivery & Billing
3.2.4 Assign Document Pricing Procedure to Billing type
SPRO –> Sales and Distribution –> Basic Functions –> Pricing Control –>Define And Assign Pricing Procedures –> Assign Document Pricing Procedures to Billing Types
We will assign the Billing Doc. Pricing Procedure “ST” to our IC STO Billing type “CBST”
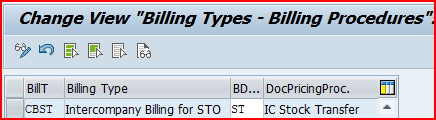
3.2.5 Assign Pricing Procedure
Now we will assign pricing procedure to “inter-company STO with Billing” scenario .
We have already defined our pricing procedure “A17J11” for “inter-company STO with Billing” in the heading 2.3 Pricing Procedure for Inter-Company STO Billing
To assign the pricing procedure follow the below path
SPRO –> Sales and Distribution –> Basic Functions –> Pricing –> Pricing Control –>Define And Assign Pricing Procedures –> Set Pricing Procedure Determination
Alternatively use transaction code OVKK
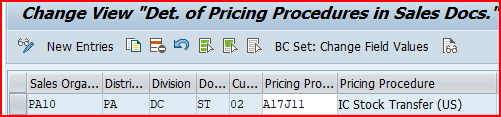
FAQ on Sales Pricing Procedure
Yes. This is possible and a normal scenario in various implementation. Please see details below
1)-Configure different document pricing procedure for sales order & billing as shown in above screenshots
2)-During Copy Control between your Del type to Billing type (VTFL), the pricing type should be B (carry out new pricing) if delivery related billing.
3)-During Copy Control between your Ord type to billing type (VTFA), the pricing type should be B (carry out new pricing) if order related billing.