In this post we will configure SAP S4 HANA MM Tax in 7 Easy Steps
How to configure SAP S4 HANA MM Tax in 7 Easy Steps
- Step 1- Introduction – What is SAP S4 HANA MM Input Tax
In this step we will see the difference between two types of SAP S4 HANA MM input tax -Jurisdiction Tax (Used in USA) & VAT (Used in EU)
- Step 2- FI related configuration of SAP S4 HANA MM Input Tax
In this step we will configure Tax Jurisdictions, FI Tax calculation Procedure, Tax code configuration & condition records creation
- Step 3- MM related configuration of SAP S4 HANA MM Input Tax
In this step we will configure all necessary parameters for automatic Tax code determination in PO and to bring the Tax amount from FI Tax calculation procedure to PO Price determination.
- Step 4- Master Data Requirement
In this step we will look into the master data requirement
- Step 5- Testing of SAP S4 HANA MM Input Tax
In this step we will test Automatic Tax ode determination, Tax amount calculation & flow of tax amount from Tax calculation procedure to PO Price determination.
- Step 6- Accounting Entries related to SAP S4 HANA MM Input Tax
In this step we will check accounting entries related to mm input tax at the time of Goods Receipt as well as at the time of invoice receipt.
- Step 7- FAQ
In this step, various FAQs related to MM input tax are answered.
Input tax (Purchase Tax) is levied on all types of purchases and output tax (Sales Tax) is levied on all types of sales. Every country follow its own sales tax, purchase tax procedure.
Table of Contents
1. introduction to SAP MM Input Tax
At a broad level, there are two types of input tax
- Jurisdiction Tax (Used in US/Canada)
- Non- jurisdiction Tax (VAT in EU)
The choice of methods is a parameter in configuring the country’s global settings
To check the detail difference between Jurisdiction Tax (Used in USA) & VAT (Used in EU), Please check FAQ section at the end of the post.
In this post we will look in detail into Jurisdiction Tax (Used in US/Canada), which is more complex to configure compare to VAT configuration.
1.1. Jurisdiction Tax (Sales & Use Tax in USA)
With this method, you manually define the jurisdiction for every region in which you do business.
US follow Jurisdiction tax where tax authority is different for each area and tax authority decides tax percentage in that area.
Jurisdiction Tax is applicable at County level, City level, state level etc. in SAP Each tax authority is created as a tax jurisdiction code in sap.
There are three type of taxes in US
- A/P Sales Tax (MM input Tax)
- Use Tax
- Self -Assessment Tax
Out of these three taxes US sales tax is MM input tax (Since we are purchaser, then our vendors collect and remit the collected tax to tax authorities) Hence it is classified as A/P MM input tax
Let,s configure & test A/P Sales Tax (MM input Tax) in the post.
1.1.1 A/P Sales Tax (MM input Tax) in SAP S4 HANA
If a transaction is happening within a state, then Sales tax is levied on the sale of taxable goods and is imposed by the tax authorities.
If we are purchaser, then our vendor should collect and remit the collected tax to tax authorities.
As vendor is responsible to collect the A/P sales tax , so at the time of incoming invoice posting in Sap S4 HANA MM module , Vendor Account will be debited cost of material + Applicable A/P Sales tax (MM input Tax)
Credit side is handled two ways in SAP S4 HANA
1.1.1.1. Non-deductible A/P Sales tax (MM input Tax)
Non-deductible tax is not refunded or offsetting against liabilities by tax authorities , so this tax is treated as extra cost . Therefore, the non-deductible part of the tax is added to the stock value during the inventory posting.
1.1.1.2 Deductible A/P Sales tax (MM input Tax)
The deductible tax amount is not to be considered as a cost item of the procurement. This tax is levied within the state
In this post we will configure & test Non-deductible A/P Sales tax (MM input Tax) (1.1.1.1. in the above two)
Let,s start with FI related configuration first.
2. FI related Configuration of SAP S4 HANA MM Input Tax
Let,s first do FI related configuration for the MM input tax
2.1 Assign Tax Jurisdictions to Regions
First of all We need to assign our plant regions to the tax Jurisdictions. We have three plants for our car business. The three plants have the below regions
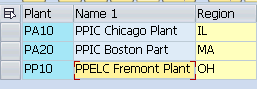
So we will assign the Jurisdictions to these regions
Assigning tax Jurisdictions to Regions helps in automatic determination of Tax codes in Purchase Orders.
SPRO -> Cross-Application Components -> SAP Business Partner -> Business Partner -> Basic Settings -> Tax Jurisdictions -> Using SAP Software -> Assign Tax Jurisdictions to Regions and Postal Codes -> Assign Tax Jurisdictions to Regions

2.2 Check Calculation Procedure
We have to first select a Tax schema to calculate the taxes. We will use SAP standard Tax schema w. Jurisdictions given by SAP
SPRO–> Financial Accounting –> Financial Accounting Global Settings –> Tax on Sales/Purchases –> Basic Settings –> Check Calculation Procedure
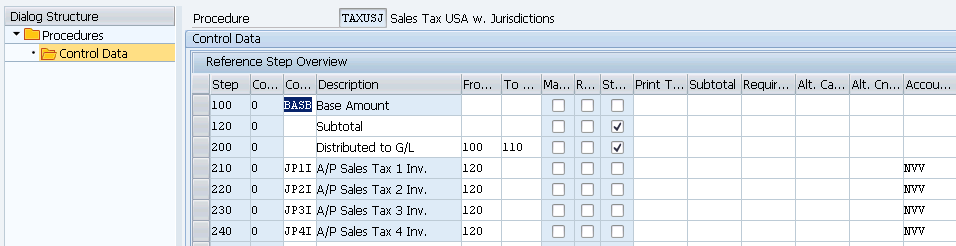
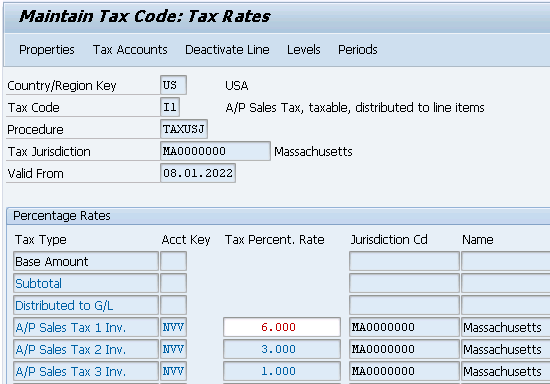
Note : The above given tax procedure is SAP standard. Mostly this serves the purpose. Generally 3 Tax condition types (S.No. 210, 220 & 230 in the above) are used to configure US input tax with Jurisdictions. See the details below
- A/P Sales Tax 1 Inv. with 6% for state (JP1I).
- A/P Sales Tax 2 Inv. with 1% for county (JP2I).
- A/P Sales Tax 3 Inv. with 1% for city Taxes (JP3I).
2.3 Assign Country/Region to Calculation Procedure
We need to assign our county “US” to the calculation procedure.
We will select the standard Tax scheme given in system for US and make the necessary changes for automatic determination of Tax code in the purchase orders & subsequently automatic tax calculation.
SPRO–> Financial Accounting –> Financial Accounting Global Settings –> Tax on Sales/Purchases –> Basic Settings –> Assign Country/Region to Calculation Procedure
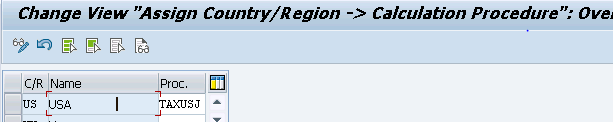
Since Tax procedures are used at country level so We have used same tax procedure "TAXUSJ-Sales Tax USA w. Jurisdictions" for SD output tax configuration Click below to check our SD tax configuration in detail Configure SAP S4 HANA SD Output Tax in 6 Quick Steps
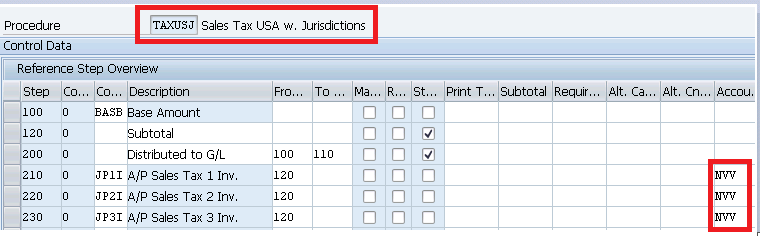
2.4 Check and Change Settings for Tax Processing
Here we make the necessary specifications for posting taxes.
We have used NVV key for all our three tax level i.e. County level, City level, state level

2.5 Define Tax Codes for Sales and Purchases
We will configure below two input tax codes
- I0 – A/P Sales Tax, exempt
- I1 – A/P Sales Tax,taxable, distributed to line items

First Created I0 tax code for Massachusetts Tax Jurisdiction.
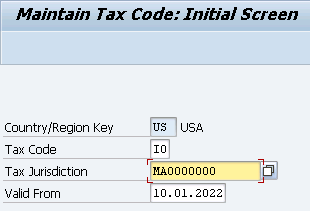
Press Enter and you will be presented below screen
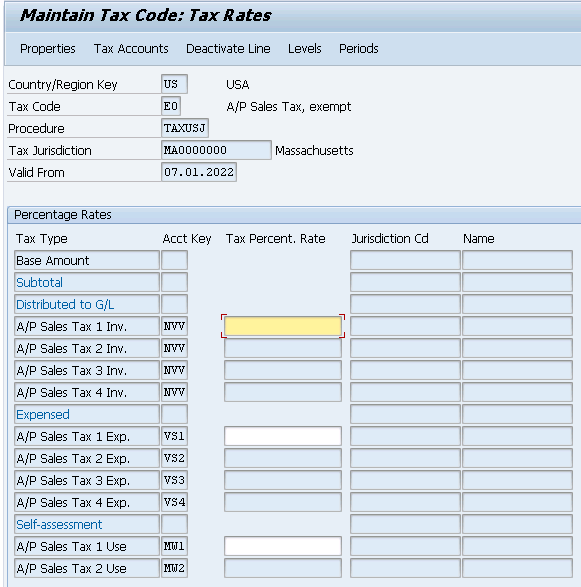
Note : In the above screen do not fill any value (for both I0 & I1). just save it . This will get value automatically once we will maintain FV11 for our Condition Types given in Tax procedure. We will see this soon.
Complete the above for the below Combination
| I0 MA0000000 | |
| I1 MA0000000 | |
| I0 OH0000000 | |
| I1 OH0000000 | |
| I0 IL0000000 | |
| I1 IL0000000 |
2.6 Condition Record Creation (FV11)
We need to create condition records for all the three Condition Types of Tax schema
Below Condition records will be created
- A/P Sales Tax 1 Inv. with 6% for state (JP1I) for all our 3 Tax Jurisdictions.
- A/P Sales Tax 2 Inv. with 1% for county (JP2I) for all our 3 Tax Jurisdictions.
- A/P Sales Tax 3 Inv. with 1% for city Taxes (JP3I) for all our 3 Tax Jurisdictions.
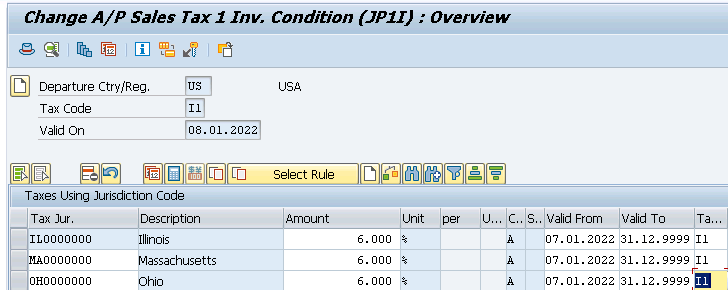
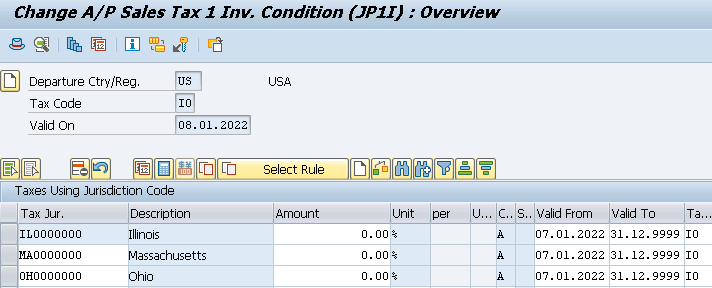
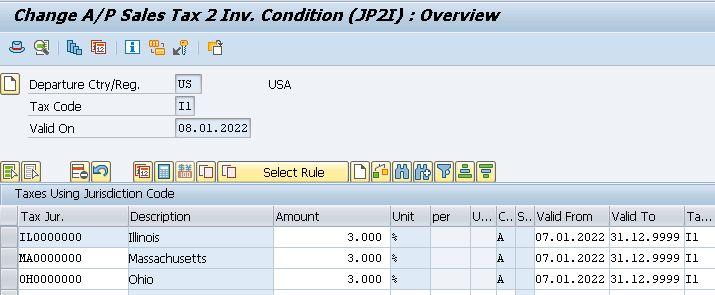
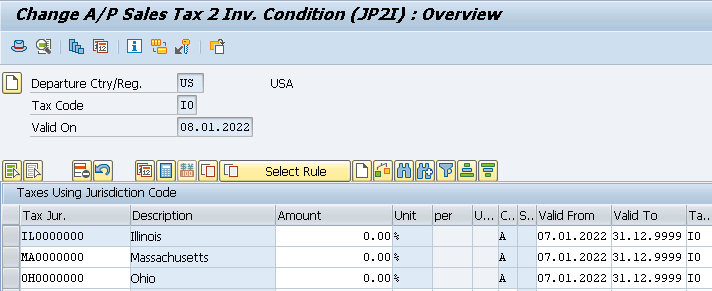
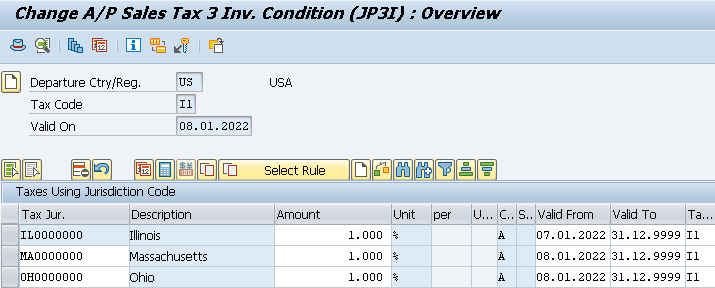
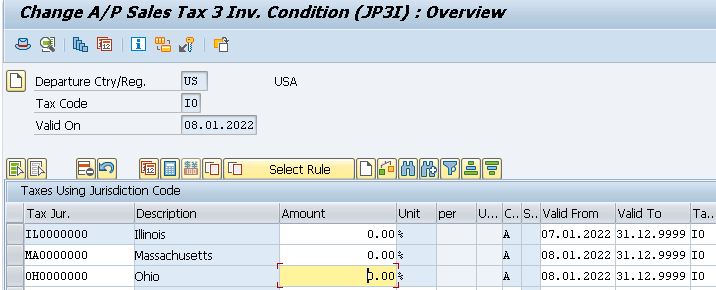
Once you maintained the above check the FTXP. It is maintained automatically
FI configuration related to S4 HANA MM Input tax is completed now.
Let,s check the MM configuration
3. MM Related Config. of SAP S4 HANA MM Input Tax
We need to do the below configuration in order to be able for the system to calculate the input tax automatically in the Purchase Oder
3.1 Condition Types Related to MM input Tax
We will use two Standard Condition types * NAVS - To bring the tax amount from the tax procedure to MM pricing procedure so that tax amount can be displayed in PO * MWVZ - To Determine the Tax Code in PO Automatically through standard MEK1)
3.1.1 Condition Type to bring Tax amount in Purchase Order
Tax amount is calculated in Tax schema. The system only calculates the non-deductible part of the tax. This amount should be regarded as an additional cost item of the procurement because the tax authorities do not refund this amount unlike the deductible part of the tax. Therefore, the non-deductible part of the tax is added to the stock value during the inventory posting. In the purchase order item, the non-deductible tax amount is saved in field EKPO-NAVNW
NAVS is the condition type which brings the value of the calculated tax to the PO field EKPO-NAVNW , if configured as per below configuration.
o Condition class "D" (taxes) o Calculation rule "B" (fixed amount) o Condition Category "N" (Input Tax not Deductible) o Manual entries "D" (cannot be edited manually) o Item condition "X" o Do not assign an access sequence o Exclusion "N" (Tax Code)
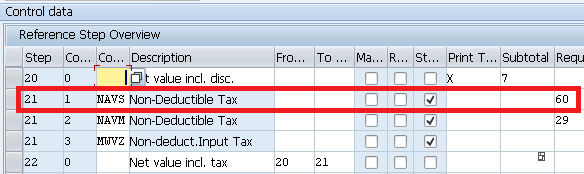
Note : Please ignore NAVM as we want to calculate and flow the tax to PO automatically. NAVM is the manual Condition type
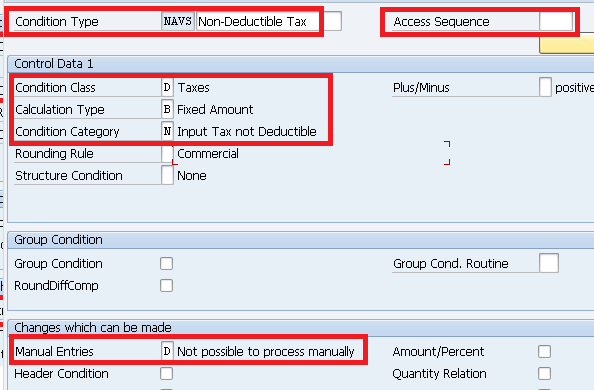
3.1.2 Condition Type for Automatic Determination of Tax Code in PO
We will do configuration to determine the tax code automatically in the PO item. Please note that the tax code can be defaulted from the purchasing info record also in the purchase order item. We will create condition records through MEK1 to determine Tax code automatically in the PO.
During the determination via the condition technique an access sequence is assigned in the standard system of condition. Assign access sequence 0003 to our condition type MWVZ
Insert this condition type in our pricing procedure
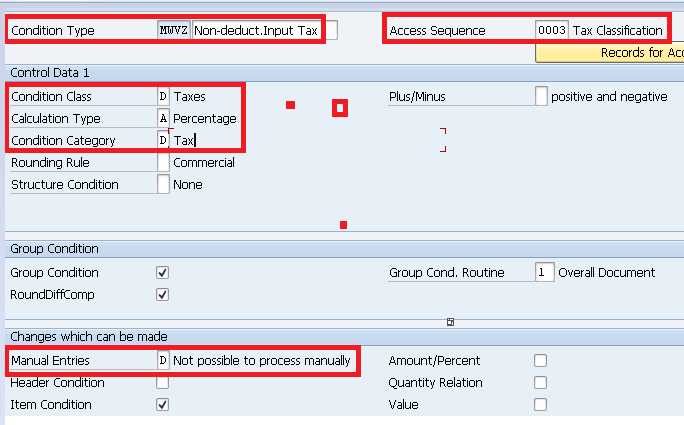
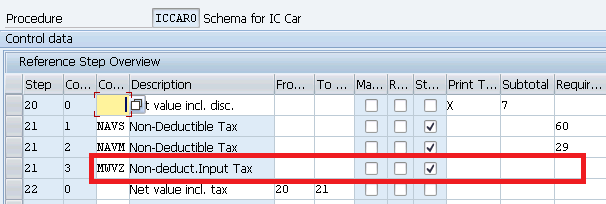
Note : Please click HERE to check the configuration of price determination procedure.
3.1.3 Supporting Configuration for Automatic Tax Determination in PO
Below configuration is required for automatic tax code determination in PO in S4 HANA MM
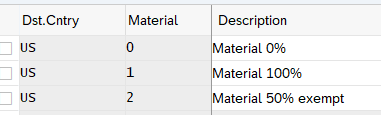
3.1.3.1 Setting Tax Indicator for Material
Here we maintain the tax indicators for corresponding materials, specific to each destination country

We have created below three Tax indicator for our companies
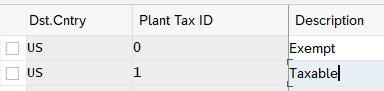
3.1.3.2 Setting Tax Indicator for Plant
Here we maintain the tax indicators to assign to plants. This is done for each country of destination
For our three plants we have maintained below two tax indicators

3.1.3.3 Assigning Tax Indicators for Plant
Here we assign tax indicator to each of our three plants
To promote clean fuel, our Electric car plant is tax free
Maintain Tax indicator for plants as below

Out both IC Car plants are taxable
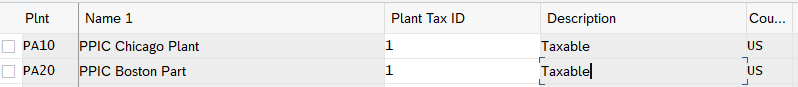
Configure Electric car plant as Tax exempt

3.1.3.4 Condition Record to determine Tax code automatically in PO
MEK1
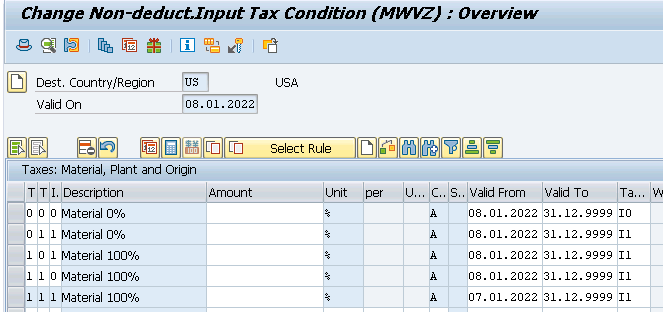
4. Master Data Requirements
In the material master purchasing view maintain the “Tax ind. f. mater” field
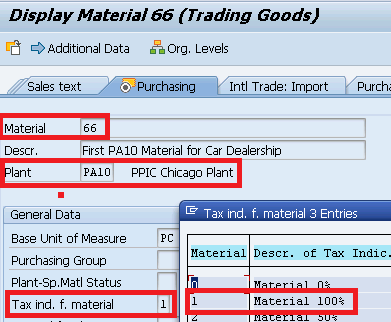
- Plant Tax indicator is coming from configuration as explained in the post.
- Import indicator logic is hard coded in SAP system.
5. Testing of MM Input Tax
Create a Purchase order for material “66” and vendor “PA01VEN03”
5.1 Automatic Tax Code Determination
System has correctly determined tax code as “I1” automatically as per the condition type values explained HERE.

To check how system has considered condition type & record to determine tax code automatically go to “Conditions” tab and click on “Analysis”
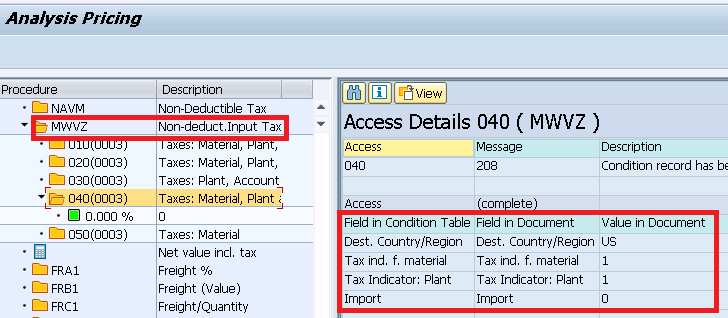
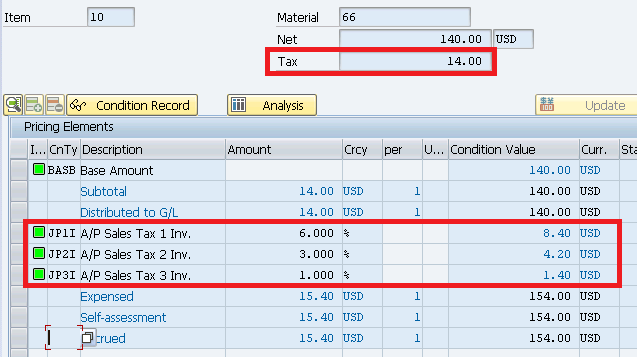
5.2 Tax Calculation Check
Click on Taxes on Invoice Tab
System has successfully calculated all the three taxes as required and total.
5.3 Flow of Tax amount from Tax Procedure to Pricing Procedure
Te amount of tax calculated shown in the previous step should flow to the PO Pricing procedure (under NAVS condition Type).
To check this click on conditions
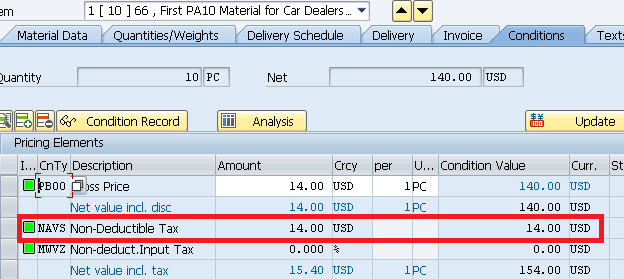
6. Accounting Entries
Post The Goods Receipt. System will create the material document & corresponding FI Document. Similarly when the enter raise invoice so at the time of entering invoice , system will post the documents.
First we need to create a Purchase order to check the good receipt & invoice entry accounting entries.
Please note that this PO is different from the previous PO created at the Point 5.
We have created PO in the post Ultimate guide to configure S4 HANA MM-FI Integration . You can check the details of the PO price and it’s components HERE
In the PO created in the above link , Tax code is determined automatically as “I1”.
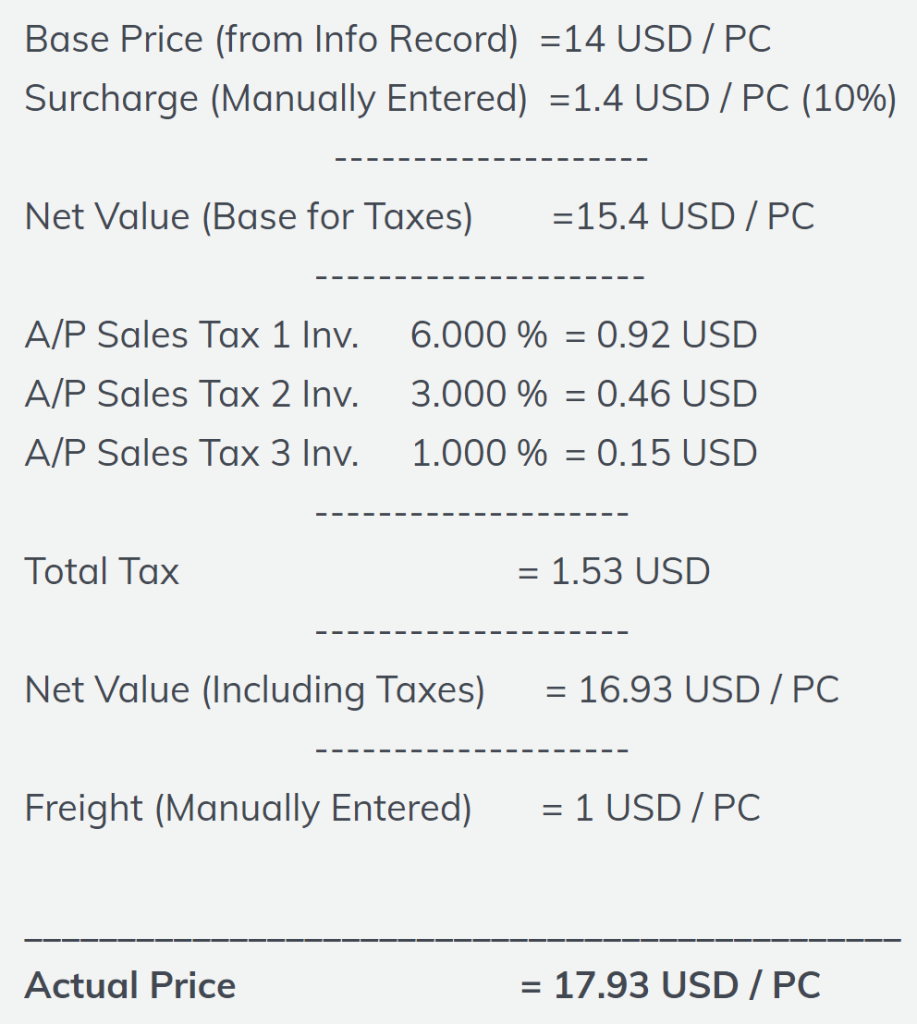
Tax calculations in PO (shown below)
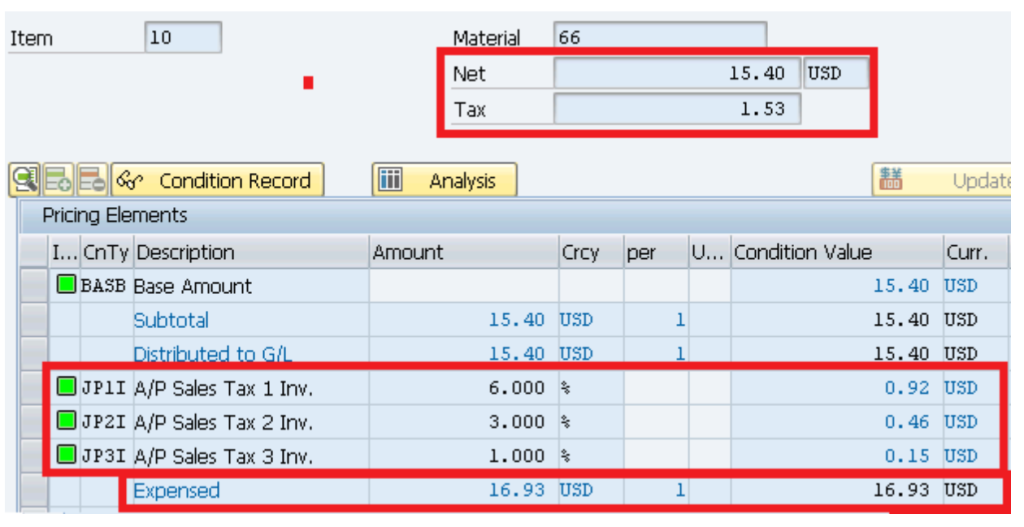
This calculation of tax of USD 1.53 is brought into PO MM price determination procedure (Picture Below) from the FI Tax determination procedure (Picture Above) through condition NAVS to calculate the total value of material. This is fully explained in the post above
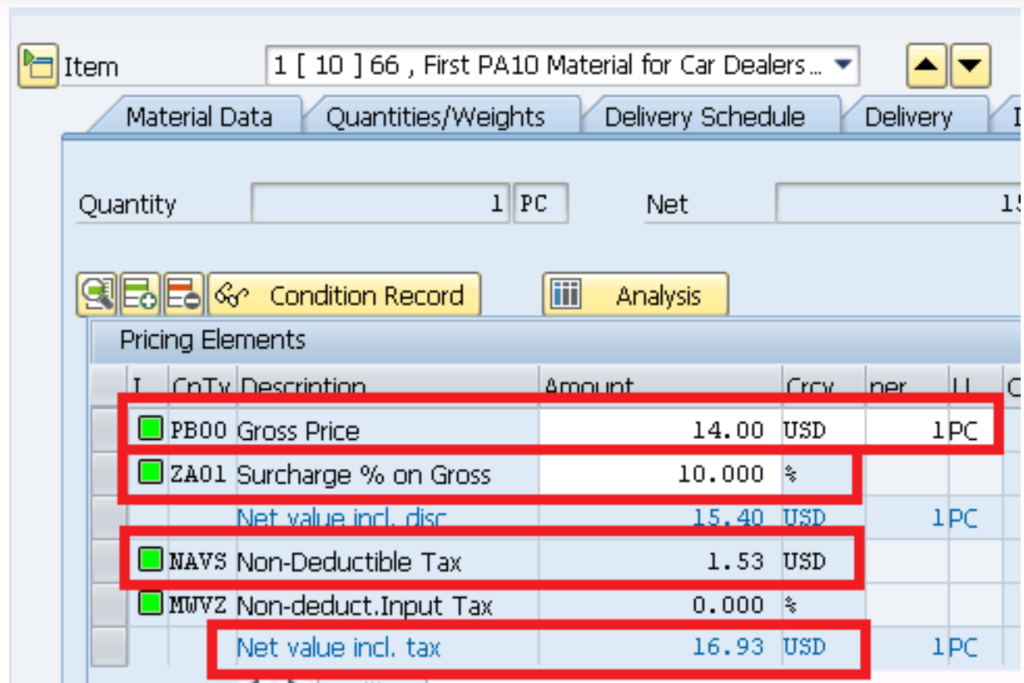
Below is the summary of full PO Price components. We will refer this to check the GR accounting entries as well as invoicing accounting entries
Tax Postings at Goods Receipt (GR)
Below is the FI document generated after posting the Goods Receipt (MIGO)
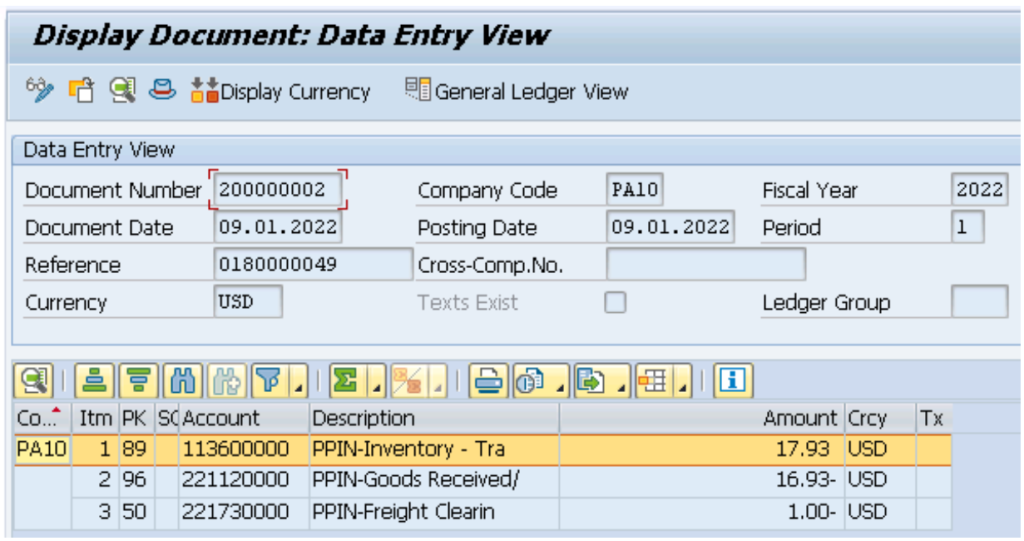
As expected & explained in the post, system has added the tax value to the material value and debited the cost to the inventory
Credit to the GR IR/IR account , which will be cleared at the time of invoicing.
Tax Postings at Invoice Receipt (IR)
Below is the FI document generated after posting the Invoice (MIRO)
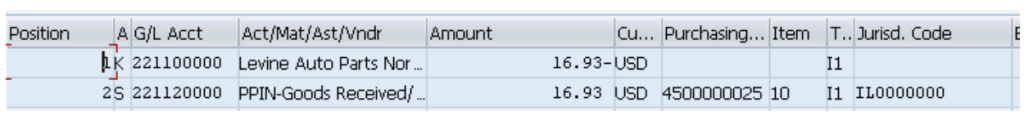
Tax amount (including material value) is credited to vendor , as expected because vendor is responsible to collect A/P input tax.
7. FAQ on Input Tax
We get the offset of deductible tax amount so system does not include this in material landing price calculation.
Example – PO pricing: Basic – USD 100
Input Tax (16%) – USD 16 (Deductible)
Since input tax is deductible, NAVS condition value in PO pricing will be 0.00.
Goods Receipt:
Credit GR/IR Account – USD 100
Debit Inventory Account – USD 100
(Input tax is not loaded on Inventory due to deductible tax)
Invoice Receipt:
Credit Vendor – USD 116
Debit GR/IR Account – USD 100
Debit VAT Credit Pool Account – USD 16
System calculate non-deductible tax and inserted the amount under non-deductible tax amount in PO. So Non-Deductible tax is included in landing price calculation and loaded on inventory i.e. included in material valuation as shown through FI document posting in the post.
* Sales tax is state level, plus thousands of local jurisdictions; VAT is only levied at the country level.
* Sales tax is set by the US states – 45 of the 50 US states, plus DC, have a sales tax. However, and this is where sales tax gets very cluttered. Counties, cities and a number of other special jurisdictions (in excess of 12,000) have the right to set and charge tax on the transaction on top of the state sales tax.
This makes the determination of the right sales tax rate a huge challenge as the business must determine exactly which jurisdictions’ taxes apply, and how to combine them. VAT is controlled and levied at the federal government only.
* Huge diversity of sales tax rates, with frequent changes. While only three or fewer VAT rates and changes are rare.
* Sales tax only on final consumer; VAT is collected on all transactions.
This is where sales tax is ‘simple’. It is only charged on the final consumer (at the till or online checkout).
In the Previous post, we have completed Business Partner & CVI related configuration. Please click on the above button to see the details
In the next post we will configure S4 HANA MM Pricing procedure.
Image Courtesy : Business vector created by macrovector – www.freepik.com







